LLMapper
An experiment in using LLMs, wikipedia and promptulate to draw simple concept maps.
LLMapper is a crude prototype for refining the prompts. Which is to say, this isn't (yet) a serious tool; it's a toy for learning about generative AI.
It's very early days. Among other things, there's no error detection or graceful failures. Use at your own risk.
Online Demo
You can see the online demo https://pne-llmapper.streamlit.app/ and source code.
The Musk search operation effect is as follows:
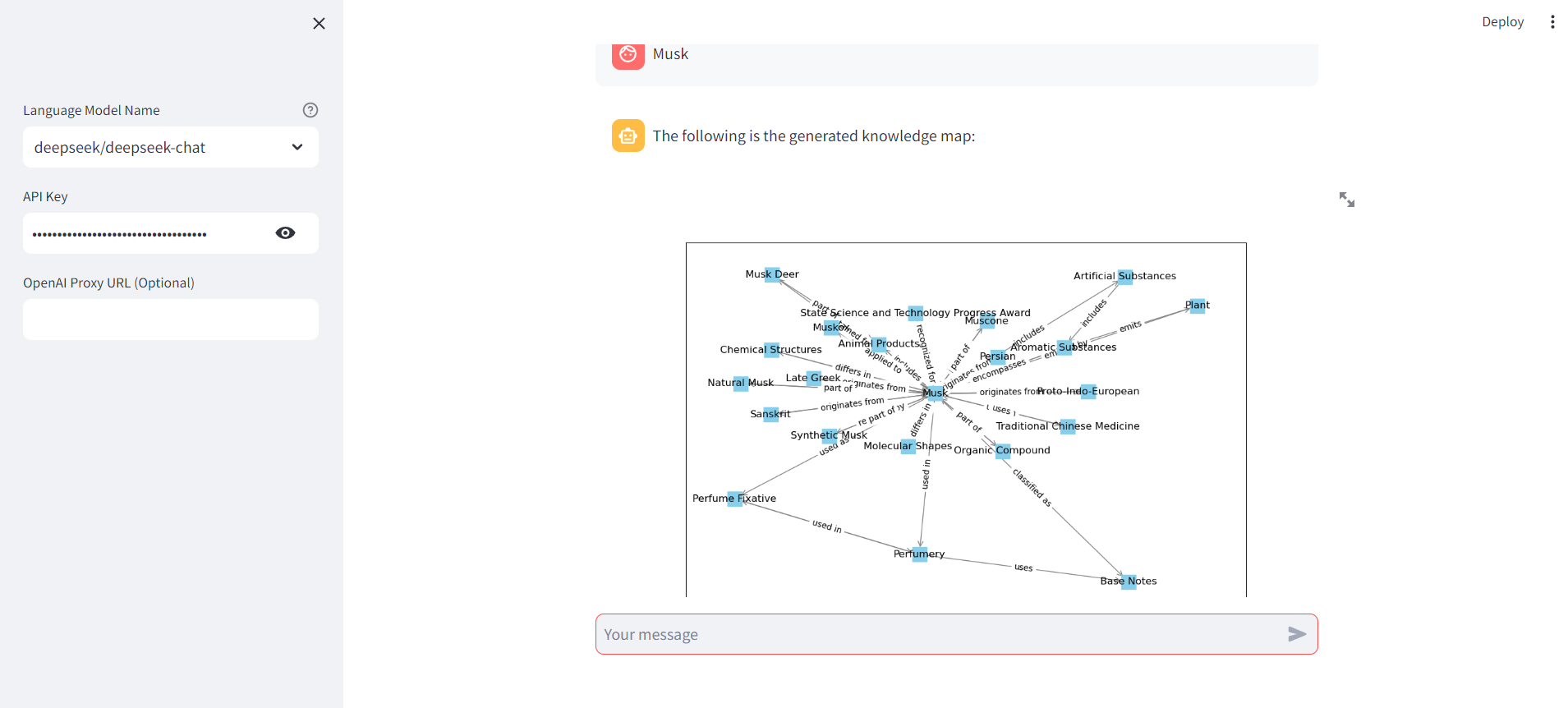
Step-by-Step Implementation

Step 1
Create a core.py script and import the necessary dependencies:
from io import BytesIO
from typing import List
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import networkx as nx
from pydantic import BaseModel, FieldDefine core classes and functions for mapping knowledge
# Fixed the matplotlib font display issue
matplotlib.use("Agg")
class AppConfig:
model_name: Optional[str] = None
api_key: Optional[str] = None
api_base: Optional[str] = None
class Node(BaseModel):
id: str = Field(..., title="ID")
title: str = Field(..., title="Title")
class Edge(BaseModel):
from_: str = Field(..., title="From", alias="from")
to: str = Field(..., title="To")
title: str = Field(..., title="Title")
class Graph(BaseModel):
nodes: List[Node] = Field(..., title="Nodes")
edges: List[Edge] = Field(..., title="Edges")
def create_knowledge_graph(graph: Graph):
graph: dict = graph.model_dump()
G = nx.DiGraph()
for node in graph["nodes"]:
layer = node["id"]
G.add_node(node["id"], title=node["title"], layer=layer)
for edge in graph["edges"]:
G.add_edge(edge["from_"], edge["to"], title=edge["title"])
return G
def draw_graph(G):
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, weight="layer")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, node_shape="s", node_color="skyblue", ax=ax)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(
G, pos, edge_color="gray", arrowstyle="->", arrowsize=15, ax=ax
)
# Draw node label
labels = nx.get_node_attributes(G, "title")
nx.draw_networkx_labels(G, pos, labels=labels, font_size=12)
# Draw the label of the edge
edge_labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, "title")
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G, pos, edge_labels=edge_labels, font_size=10, ax=ax)
buf = BytesIO()
fig.savefig(buf, format="png")
buf.seek(0)
return buf
def generate_nodes(query_result: str, app_config: AppConfig) -> Graph:
_prompt = f"""
Please generate a knowledge graph based on the requirements of {summary_prompt}
and the content of {query_result}
"""
return pne.chat(
model=app_config.model_name,
messages=_prompt,
model_config={"api_base": app_config.api_base, "api_key": app_config.api_key},
output_schema=Graph,
)Step 2
Create a prompt-summarize.md script:
# MISSION
You are an expert summarizer. You will examine an article and produce a list of concepts about the article and a list of relationships between those concepts.
# INPUT
You will be given the text of an article. This will be the sole source of information for your outline. Do not include any details that don't appear in the article.
# CONTEXT
Treat everything in the article as factual.
# METHODOLOGY
1. Start by summarizing the article.
2. Make a list of all concepts described in the article.
- A concept is a common or proper noun
- A concept cannot include more than one noun (it cannot include lists of nouns)
3. Focus only on the concepts that are most relevant to what this article is about and why it matters.
4. The first concept in the list is the main subject of the article
5. Take the first concept in the list and consider its relationship to all the other concepts in the list, and list the hierarchical relationship between the first concept and all the other concepts
6. Do the same thing for the second concept, and then every remaining concept in the list.
# OUTPUT
- Combine all of your understanding of the subject being summarized into a single, 20-word sentence. Do NOT mention the summary itself; focus only on the subject. Write it in a section called WHAT THIS IS:.
- Speculate about why this subject matters and write a single 20-word sentence that explains it in a section called WHY IT MATTERS:.
- Choose the 10 MOST IMPORTANT concepts in the article in order of importance. A concept is a common or proper noun that is a key part of the article. The most important concepts are those that help explain what this is and why it matters. Only include one concept per bullet. Don't include descriptions of each concept; only the concepts themselves. Include concepts that explain why this subject matters. The first concept in the list is the main subject of the article. Output the list in a section called MAIN CONCEPTS:.
- Write a list of how each concept in the MAIN CONCEPTS list relates to each of the other concepts in that list and their hierarchy.The hierarchical relationship between each concept is represented by an Arabic numeral corresponding to the id= hierarchy. ONLY USE CONCEPTS FROM THE CONCEPTS LIST. Do not introduce new concepts. Add each relationship to a list in the format "noun verb noun." DO NOT WRITE SENTENCES, only noun-verb-noun. Only include one object and subject in each bullet point. Consider how this concept relates to the main subject. Include relationships that help explain why this subject matters. Output that list in a section called RELATIONSHIPS:.
This is the format for the RELATIONSHIPS section:
- Bytedance owns TikTok
- Bytedance owns Douyin
- TikTok expanded globally
Only include ONE SUBJECT, ONE OBJECT, and ONE PREDICATE per bullet. Do not include adjectives or adverbs. Do not include lists in bullets.
Include as many relationships as necessary to represent ALL the concepts in the concepts list. Include at least 20 relationships in this list. DO NOT INCLUDE CONCEPTS THAT AREN'T PRESENT IN THE CONCEPTS LIST ABOVE.
# RULES
- Do not mention the article itself
- Do not mention references
- Write the summary in Markdown formatStep 3
Create a app.py script and define the sidebar to place the user parameter configuration:
import streamlit as st
from core import (
AppConfig,
Graph,
create_knowledge_graph,
draw_graph,
generate_nodes,
)
from promptulate.tools.wikipedia import wikipedia_search
def main():
app_config = AppConfig()
with st.sidebar:
app_config.model_name = st.selectbox(
label="Language Model Name",
options=[
"openai/gpt-4o",
"openai/gpt-4-turbo",
"deepseek/deepseek-chat",
"zhipu/glm-4",
"ollama/llama2",
],
help="For more details, please see"
"[how to write model name?]("
"https://www.promptulate.cn/#/other/how_to_write_model_name)",
)
app_config.api_key = st.text_input(
"API Key", key="provider_api_key", type="password"
)
app_config.api_base = st.text_input("OpenAI Proxy URL (Optional)")
"[View the source code](https://github.com/Undertone0809/promptulate)"
st.title("llmapper")
st.caption(
"""
llmapper was an experimental project. Given a query term, llmapper would search Wikipedia for relevant content, and then generate a knowledge graph using Promptulate.\n
🚀 Power by [promptulate](https://github.com/Undertone0809/promptulate)
""" # noqa
)
st.chat_message("assistant").write(
"Input the query you want to generate a knowledge graph for."
)
if prompt := st.chat_input():
if not app_config.api_key:
st.info("Please add your API key to continue.")
st.stop()
st.chat_message("user").write(prompt)
st.chat_message("assistant").write(f"Querying {prompt} from Wikipedia...")
query_result: str = wikipedia_search(prompt, top_k_results=1)
st.chat_message("assistant").write(
f"Found the following content from Wikipedia:\n{query_result}"
)
st.chat_message("assistant").write(
"Generating knowledge graph based on the query result..."
)
graph: Graph = generate_nodes(query_result, app_config)
# generate and draw the knowledge graph
G = create_knowledge_graph(graph)
buf = draw_graph(G)
st.chat_message("assistant").write(
"The following is the generated knowledge map:"
)
st.image(buf)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Finally, run the application:
streamlit run app.pyQuick Start
You can use the following command to run the LLMapper project quickly:
Click here to fork the project to your local machine
Clone the project locally:
git clone https://github.com/Undertone0809/promptulate.git- Switch the current directory to the example
cd promptulate/example/llmapper- Install the dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt- Run the application
streamlit run app.py